The Odyssey with AI Agents
Introduction
Expedition in a nut-shell
AI agents are transforming the way tasks are performed, operating with autonomy or minimal human intervention. By leveraging machine learning, NLP, and other AI techniques, they can perceive their environment, process information, make decisions, and take actions. Their ability to continuously learn and adapt makes them invaluable across domains like customer service and industrial automation.
The journey with AI agents follows a structured process—perception, decision-making, action, and learning enabling them to navigate complex, dynamic environments effectively. As they evolve, AI agents are not just tools but intelligent collaborators, shaping the future of automation and efficiency.
Things Manually
AI/ML
 Highlights
HighlightsHighlights
Agentic AI represents a breakthrough in artificial intelligence, excelling at complex problem-solving, coordinating seamlessly with multiple peer agents, and acting autonomously based on environmental changes or specific objectives. This dynamic capability positions agentic AI as a pivotal force in transforming industries and driving innovative solutions.
Complex Problem Handling
AI agents excel at solving problems that require complex multi dimensional considerations and computations. Their ability to analyse vast datasets and generate optimal solutions is unparalleled.
Coordination and Collaboration
AI agents can seamlessly coordinate with multiple peer agents to converge on a desired outcome. This collaborative capability enhances efficiency and effectiveness in achieving shared goals.
Proactive execution
Unlike traditional systems that require continuous user prompts, Agentic AI can be triggered by changes in environmental states, external stimuli, or specific objectives that need to be achieved.
AI Agent Types
Simple Reflex Agents
Autocorrect agent that uses some history and current input to provide an improved outcome.
Model-based Reflex
Predicting requirements in an inventory warehouse as inventory status changes historically over time.
Goal-based agents
AlphaGO based agent that focuses on winning a game of Go.
Utility-based agents
Recommendation engines can use utility-based agents to suggest the next set of titles on a streaming platform.
Learning agents
Technology responsible for keeping spam out of your inbox.
 Introduction
Introduction Relevancy
RelevancyRelevancy
Which of these attributes best describe your problem space?
High Criticality, Low Complexity
These applications are critical, but the AI systems involved are relatively simple and well-understood. Failure can have significant consequences, so reliability is crucial. They are a good fit for a simplified single AI agent deployment.
High Criticality, High Complexity
These are the most challenging scenarios, where AI systems are both complex and critical. They require significant investments in development, expertise, and maintenance to ensure reliability and performance. AI agents are a strong fit for an environment and a problem such as this.
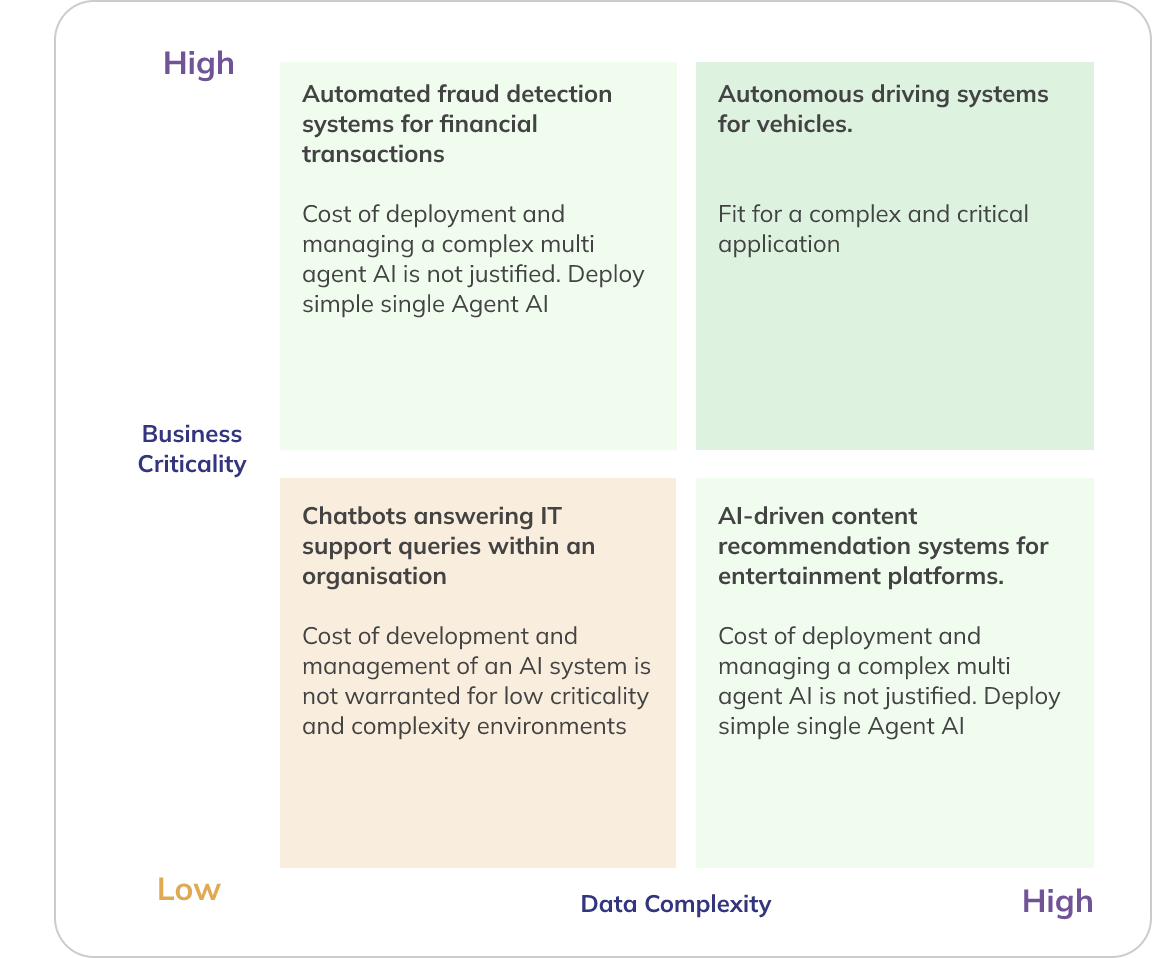
Low Criticality, Low Complexity
These are applications where the AI’s role is peripheral, and failure or errors are tolerable. The AI system is straightforward, requiring minimal resources and expertise. The cost of managing a complex AI system is often not warranted.
Low Criticality, High Complexity
The AI systems in these applications are complex, requiring specialized expertise and resources, but failures have minimal impact. Simple single AI agents are good candidates for solving problems in this cross-section.
How to proceed forward?
Things to consider
High intital cost
Generally more complex solutions to build, train and manage.
Complexity
The operational model is far complex.
Difficult to interpret
It can be difficult to interpret especially in a multi agent environment
Data dependency
Certain agents have a strong dependency on the availability of training data to ensure that data accuracy of output is within acceptable limits.
 Highlights
Highlights Preparation
PreparationPreparation
Things you need before the journey

Key Insight
Ensuring that your data is high-quality, well-organized, and comprehensive is fundamental to the success of any AI project.
 Relevancy
Relevancy Itinerary
ItineraryItinerary
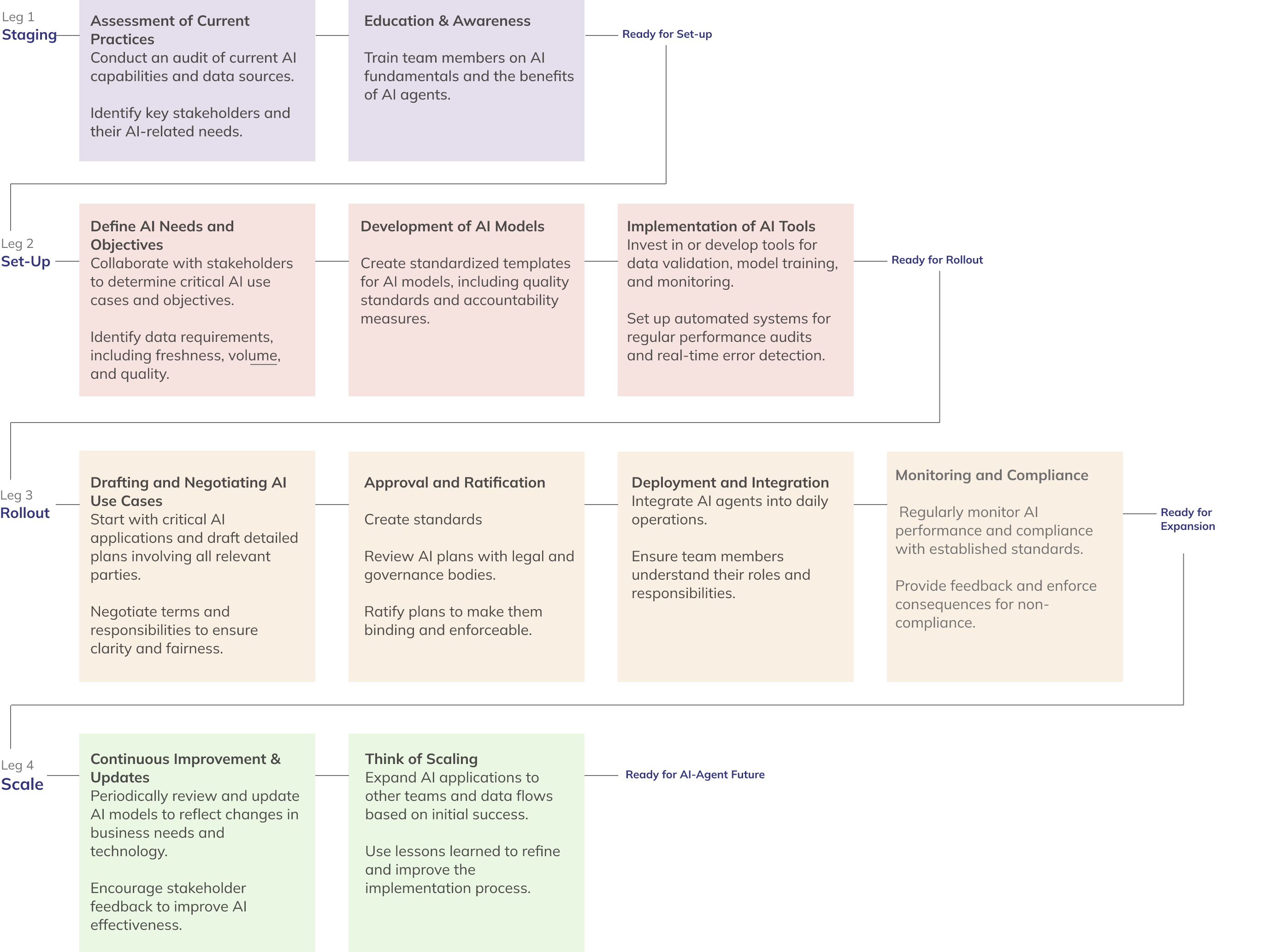
4 legs of the Journey


 RESTART
RESTART

